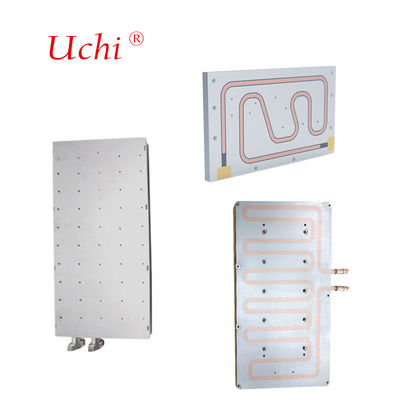
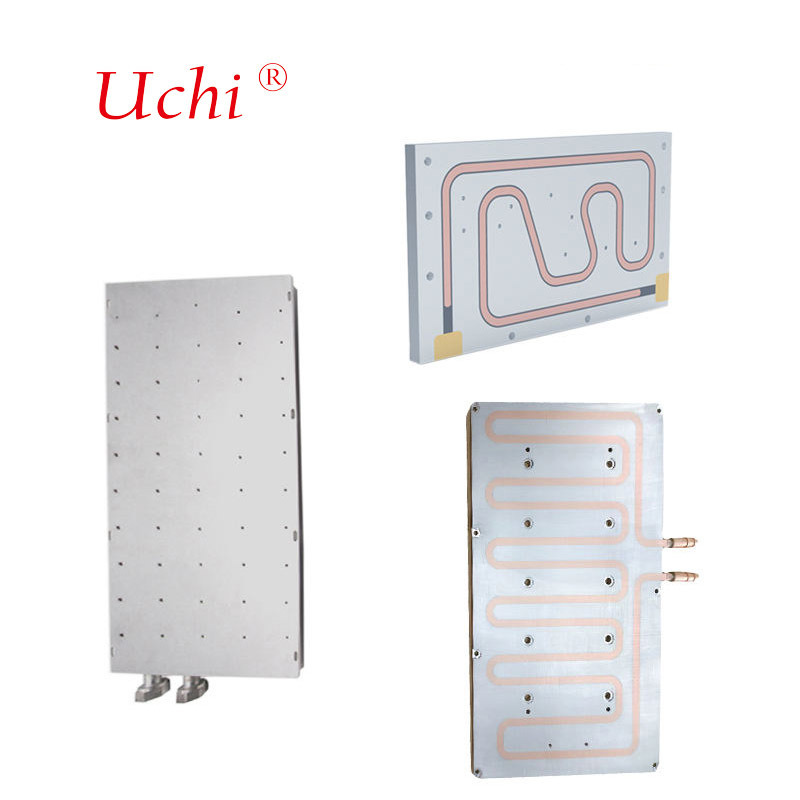
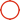
Core Heat Exchange Component Of Water-Cooled Cooling System
Product Details:
| Place of Origin: | Dongguan,Guangdong,China |
| Brand Name: | Uchi |
| Certification: | SMC |
| Model Number: | Heat Sink |
Payment & Shipping Terms:
| Minimum Order Quantity: | 100pcs |
|---|---|
| Price: | 1300-1500 dollars |
| Delivery Time: | not limited |
| Payment Terms: | T/T,paypal, Western Union,MoneyGram |
| Supply Ability: | 50000000pcs per Month |
|
Detail Information |
|||
| Heat Conducting Power: | 80W | Fan Life: | 50000 Hrs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material: | Aluminum 1060 | Size: | 158x110x60mm |
| Weight: | 0.35 Kg | Technology: | Zipper Fin |
| Certification: | ISO9001:2015 ISO9001:14001 | Surface Treatment: | Stamping + Surface Finish |
| Feature: | Flexible In Structure And Durable In Surface Treatment | ||
| Highlight: | water-cooled cooling system plate,liquid cooling heat exchange component,cooling system core heat exchanger |
||
Product Description
Core Heat Exchange Component Of Water-Cooled Cooling System
The Liquid Cold Plate is the core heat exchange component of the liquid cooling system. Through the metal substrate and internal sealed flow channel, the heat from the heating device is efficiently transferred to the circulating cooling liquid, and then dispersed to the outside world through the heat exchanger. The heat dissipation efficiency is much higher than traditional air cooling and is widely used in high power density scenarios.
basic structure and principle
Core components: bottom plate (aluminum/copper, directly attached to the heat source), internal flow channel (serpentine/parallel/microchannel), cover plate (sealed flow channel), and liquid inlet and outlet joints; commonly used cooling liquids are deionized water, water-glycol mixture.
Work flow: heat source → metal bottom plate heat conduction → flow channel wall → flowing coolant absorbs heat → coolant flows to CDU /radiator to dissipate heat → cooling back to cold plate after cooling, forming a closed loop.
Key advantages: low thermal resistance (0.02 - 0.05°C/W), high heat dissipation power, good temperature uniformity, and low noise; suitable for data centers with stand-alone cabinet power of 50kW +, AI chips, new energy vehicle battery packs, etc.
basic structure and principle
Core components: bottom plate (aluminum/copper, directly attached to the heat source), internal flow channel (serpentine/parallel/microchannel), cover plate (sealed flow channel), and liquid inlet and outlet joints; commonly used cooling liquids are deionized water, water-glycol mixture.
Work flow: heat source → metal bottom plate heat conduction → flow channel wall → flowing coolant absorbs heat → coolant flows to CDU /radiator to dissipate heat → cooling back to cold plate after cooling, forming a closed loop.
Key advantages: low thermal resistance (0.02 - 0.05°C/W), high heat dissipation power, good temperature uniformity, and low noise; suitable for data centers with stand-alone cabinet power of 50kW +, AI chips, new energy vehicle battery packs, etc.
Manufacturing Capabilities
Advanced Brazing Technology
Brass / Copper CNC
Aluminium / Zinc CNC
Stainless Steel / Steel CNC
Plastic CNC
Key Design and Performance Indicators
Flow Channel: Microchannels (<1mm) can enhance the heat transfer coefficient but increase pressure drop; serpentine flow channels offer good temperature uniformity; flow velocity and flow resistance need to be balanced.
Sealing and Pressure Resistance: 100% leak testing (helium test) is mandatory, with extremely low static leakage rate; burst pressure is typically more than three times the rated pressure.
Material Selection: Aluminum (high cost performance, light) is used for general scenarios; copper (higher thermal conductivity) is used for ultra-high heat flux density scenarios.
Flow Channel: Microchannels (<1mm) can enhance the heat transfer coefficient but increase pressure drop; serpentine flow channels offer good temperature uniformity; flow velocity and flow resistance need to be balanced.
Sealing and Pressure Resistance: 100% leak testing (helium test) is mandatory, with extremely low static leakage rate; burst pressure is typically more than three times the rated pressure.
Material Selection: Aluminum (high cost performance, light) is used for general scenarios; copper (higher thermal conductivity) is used for ultra-high heat flux density scenarios.
Want to Know more details about this product