The principle and structure of electric push rod
October 10, 2024
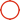
Push rod motor, also known as electric push rod or linear actuator, is an electric drive device that converts the rotational motion of the motor into linear reciprocating motion for performing mechanical operations. The following is the working principle and main components of the push rod motor:
Working Principle
1. Conversion from Rotation to Linear Motion: The core function of a push rod motor is to convert the rotational motion generated by the motor into linear motion after being reduced by a reduction gear or worm gear. This is usually achieved through the combination of a screw and a nut. The rotation of the motor drives the screw to rotate, while the nut engaged with the screw moves along the axis of the screw, resulting in linear motion.
2. Travel control: The travel of the push rod motor can be controlled through limit switches. When the push rod reaches the set stroke, the limit switch is triggered and the motor stops running.
3. Forward and reverse control: By changing the rotation direction of the motor, the push rod can be pushed and pulled back.
![]()
Main Components
1. Drive motor: Provides a power source, which can be a DC motor or an AC motor, providing different voltages and powers as needed.
2. Reduction gear: used to reduce motor speed and increase torque to generate sufficient force to push the load.
3. Screw and nut: constitute the core part of the push rod motor, where the rotation of the screw drives the nut to move in a straight line.
4. Guide sleeve: guides the nut to move in a straight line, reducing friction and wear.
5. Push rod: connected to the nut, directly applies force to the load.
6. Sliding seat: supports the push rod, allowing it to move smoothly on a fixed track.
7. Spring: Used in some designs for return or buffering.
8. Shell: protects internal components and provides structural support.
9. Turbine and micro control switch: used to control the action and stop of the push rod motor.
![]()
![]()
Characteristics and Applications
Innovative design: small size, high precision, and good self-locking performance. Energy saving: Compared to pneumatic actuators, electric push rods only require power supply to reach the desired position when controlling the opening, and can then be powered off, thus saving energy. Widely applicable: Suitable for long-distance operation, such as opening and closing of air doors, valves, gates and other mechanisms in power, chemical, metallurgical, mining, light industry, transportation, shipbuilding and other departments, material loading and unloading, flow control, etc.
Control and feedback device
Encoder: By providing feedback on the number of rotations of the motor spindle through pulse count, precise control is achieved. Potentiometer: Reflects the stroke position of the push rod, controls the push rod to stop at any position in the middle of the stroke. Hand cranked device: It adjusts the position of the push rod by hand cranking in the event of a power outage. Hall feedback: By using the Hall principle to provide feedback on the number of motor rotations, precise control can be achieved. PLC control: Provide PLC access ports to achieve real-time control.
The design of push rod motors aims to meet various industrial automation needs, and through precise control and strong adaptability, they play an important role in modern industrial automation.